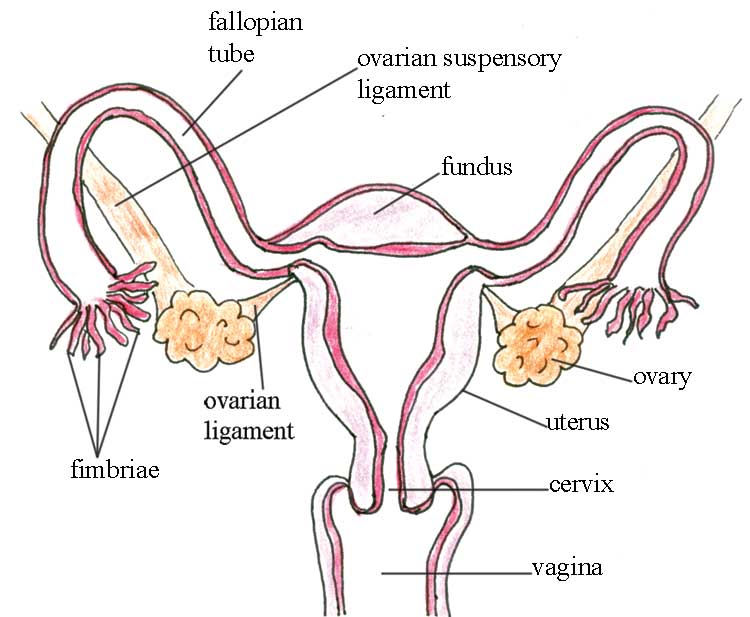

Fallopian tubes: they connect the womb with the ovaries. When an ovary releases an egg (ovum), it travels through the fallopian tubes into the womb.
Ovaries: the ovaries release one ovum into a woman's fallopian tubes each month. When a man's sperm joins the ovum, it can develop into a baby (fertilisation).
Ovarian follicles: small pits where the ova are held. These produce the female reproductive hormones oestrogen and progesterone.
Cervix: the opening of the womb or uterus.
Vagina (or birth canal): leads from the vulva to the womb. It is a muscular passage that stretches easily during sex and when giving birth. It makes a fluid (discharge) that helps keep itself clean and prevent infections.
Uterus (womb) : a hollow muscle. Monthly bleeding comes from the womb.The baby (fetus) grows here during pregnancy. Its main function is to protect and nourish the fetus until birth.