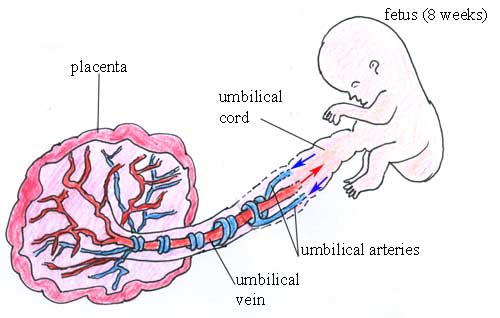

The two umbilical arteries collect deoxygenated blood from the body of the fetus and carry it to the placenta.
The umbilical vein carries oxygenated and nutrient-rich blood from the placenta and delivers it to the fetal heart, which pumps it around the body of the fetus.
The fetal capillaries in the placenta are very close to the pool of maternal blood.
The maternal blood never mixes with the fetal blood- they are separated by the walls of the fetal blood vessels.
The placenta allows the passage of some proteins including maternal antibodies that protect her and the developing fetus from getting infections during the pregnancy.
The placenta secretes the human chorionic gonadotropin hormone (HCG) which is detected in the woman's urine during a pregnancy test.