The measures described below help to protect the susceptible host either from becoming infected, or from developing the stage of infectious disease if they are exposed to the infectious agents.
You will learn more about vaccine-preventable diseases in Study Sessions 3 and 4 of this Module.
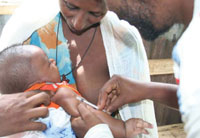
As you already know from Study Session 1, vaccination refers to administration of vaccines to increase the resistance of the susceptible host against specific vaccine-preventable infections. For example, measles vaccination helps to protect the child from measles infection, and BCG vaccination gives some protection from tuberculosis (Figure 2.4).

Chemoprophylaxis is pronounced 'keem-oh-proff-ill-axe-sis'; ('chemo' refers to medical drugs, and 'prophylaxis' means 'an action taken to prevent a disease').
Chemoprophylaxis refers to the drugs given to exposed and susceptible hosts to prevent them from developing an infection. For example, individuals from non-malarial areas who are going to a malaria endemic area can take a prophylactic drug to prevent them from developing the disease if they become infected with malaria parasites from a mosquito bite.
Proper nutrition and exercise improves a person's health status, supports the effective functioning of their immune system, and increases resistance to infection.
Measures taken to decrease contact with reservoirs of infection include:

Now you have many good ideas on what measures can be undertaken to prevent and control communicable diseases. However, you have to apply these methods effectively in order to prevent and control the most important communicable diseases in your community. But how do you identify these diseases? In the next section we will answer this question.