RT-PCR for Diagnosis SARS CoV-2
I. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
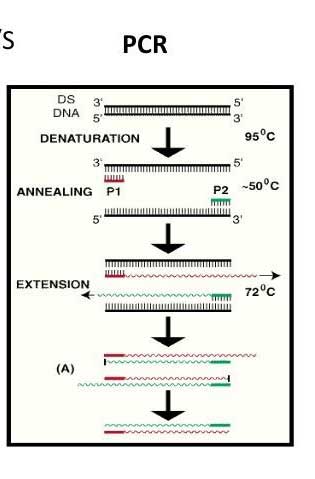
- The Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) is a process for the amplification of specific fragments of DNA
- The Driver of PCR is the Polymerase enzyme.
- A polymerase will synthesize a complementary sequence of bases to any single strand of DNA providing it a double stranded starting point
- Any gene can be specifically amplified by the polymerase in a mixed DNA sample by adding small pieces of complementary DNA
- These small pieces of DNA are known as primers because they prime the DNA sample ready for the polymerase to bind and begin copying the gene of interest
- During a PCR, changes in temperature are used to control the activity of the polymerase and the binding of primers
Click to Enlarge

