Assessment
Look, Listen and Feel for
- Unequal or poorly reactive pupils

- Blood or fluid from ear or nose
- Movement and sensation in all 4 limbs
- Blood glucose check always in the confused or unconscious patient
- Assess AVPU or Glasgow Coma Scale, GCS

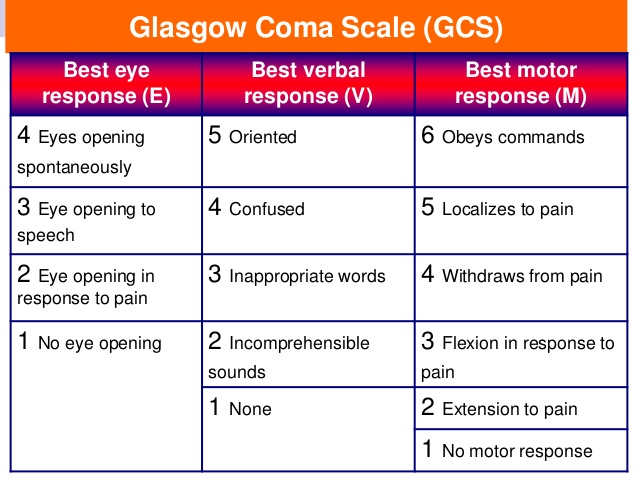
- Assess for Confusion, lethargy or agitation
Management
- If GCS<9 (or for children AVPU score of P or U), plan for advanced airway support
- If patient is lethargic or unconscious, re-assess the airway frequently
- Suspect spine injury or closed head injury with any trauma patient with altered mental status
- Give oxygen
- If low blood glucose or unable to check, give glucose
- If convulsing, give a benzodiazepine like diazepam
Examples of Conditions:
1. Severe Head Injury
Signs:
- Visual changes, memory loss, convulsions, vomiting, headache
- Altered mental status
- Scalp wound
- Skull deformity
- Bruising to head
- Blood or fluid from the ears or nose
- Unequal pupils indicating possible increased intracranial pressure
Management:
spinal immobilization, use log-roll precautions, assess changes in
level of consciousness using GCS, antibiotic cover for open skull
fracture, Nil per Os until, elevate head of the bed to 30 degrees if
suspected increased intracranial pressure, Neurosurgeon's review.
Full spine immobilization

Log-roll precautions






