A respiratory emergency is a condition in which breathing is reduced or stopped so that oxygen in taking is insufficient (lacking) to support life.

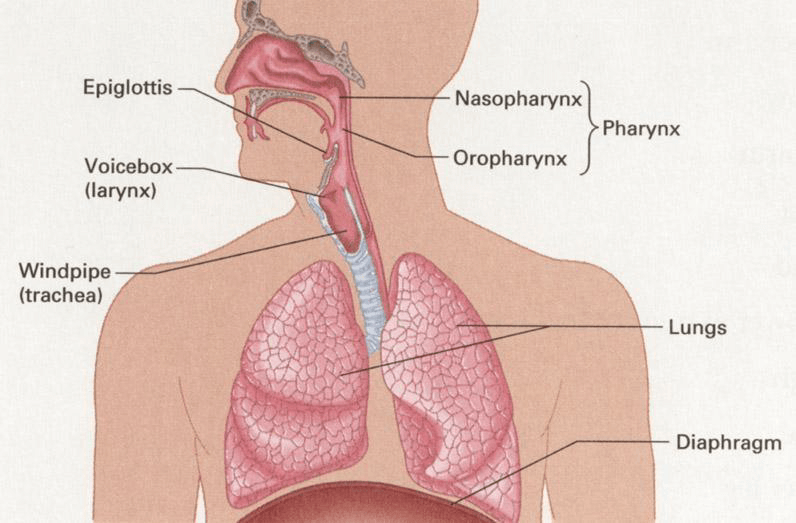
Mechanism of breathing:
During Inspiration- Air enters the nostril --> nasopharynx --> oropharynx --> through the glottis --> trachea /air pipe/ --> bronchi --> bronchioles --> alveoli.
During inspiration / inhalation/ the diaphragm and the Intercostals muscles contract, the diaphragm move down (flat), the ribs lift up and out, and the cavities of the chest and lung increases.
During expiration /exhalation/ the diaphragm and the Intercostals muscles relax, the diaphragm moves up (increase its curvature), the ribs get down, the cavities of the chest and lung capacity decreases and air move out (see Figure 23, below).
Note- The normal range of breathing at a resting condition for an adult is 14 to 20 breaths per minute, and the newborn baby has a rate of about 40 breaths per minute.
Inadequate breathing is if the number of breaths per minute / rate per minute/ is less than 8 in adults, 10 in children and 20 in infants.
Causes of airway obstruction: