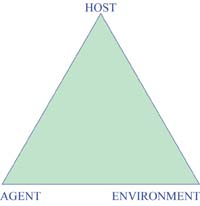
The communicable disease model presents three elements; infectious agent, host and environment, as the minimal requirements for the presence and spread of a communicable disease in a population.
The infectious agent is the element that must be present for the disease to occur and spread. Bacteria, viruses and parasites are examples of infectious agents.
The host is any susceptible organism. Plants, animals or humans can be invaded by the infectious agent and become the host.
The environment includes all other factors that either promote or prohibit disease transmission.
Communicable disease transmission occurs when a susceptible host and an infectious agent exist in an environment that allows disease transmission.

According to the communicable disease model, the role of health education and health promotion in reducing the occurrence and transmission of diseases can be brought about by specific actions.
Think of tuberculosis (TB), malaria and intestinal infections as examples, and then answer the following questions:
You may have answered with the following examples:
