The health belief model is one of the earliest and best-known health behavior models developed in the 1950's by social psychologists Hochbaum, Rosenstock and others, who were working in the U.S. Public Health Service to explain the failure of people participating in programs to prevent and detect disease. Later, the model was extended by others to study people's behavioral responses to health-related conditions. Since this time, the Health Belief Model has evolved to address public health concerns and has been applied to a broad range of populations and health behaviors.
Two major factors influence the likelihood that a person will adopt a recommended preventive health action. First, they must feel personally threatened by disease i.e. they must feel personally susceptible to a disease with serious or severe consequences. Second, they must believe the benefits of taking the preventive action outweigh the perceived barriers of (and/or cost of) preventive action.
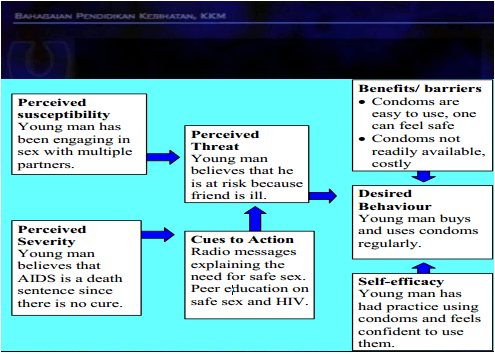
The health belief model assumes that the most important determinants of people's behaviors are their beliefs or perceptions. There are four major concepts/constructs related to perceptions and beliefs and the model is used to plan and give individual health education.
A. The perceived susceptibility --- one's perception of chances of getting the condition or a disease.
B. The perceived severity --- one's perception of how serious the condition/disease and its consequences.
C. The perceived benefit --- one's opinion of the efficacy of the advised action to reduce the risk or seriousness of the condition/disease
D. The perceived barriers --- one's opinion of the tangible and psychological costs of the advised action or behavior
E. Cues to action --- strategies to activate readiness of the individual/community for the advised action/behavior
F. Self-efficacy --- confidence on one's ability to take action.
During the application process of the model you need to do the following:
Example 1: Application of the model for HIV/AIDs --- a young man wants to use a condom (action/behavior).

Example 2: A 42 years old woman is interested to get a mammography to understand about breast cancer