Infants should be exclusively breastfed for the first six months of life to achieve optimal growth, development, and health. After that, to meet their evolving nutritional requirements, infants should receive adequate nutritionally and safe complementary foods while breastfeeding continues for up to two years of age or beyond.
During illness, children may not want to eat much. However, they should be offered the types of food recommended for their age, as often as recommended, even though they may not take much at each meal. After an illness, good feeding helps to prevent weight loss, prevent malnutrition, and prevent future illness.
Feeding recommendations from birth up to six months old
- Initiate breastfeeding within one hour after birth and the mother should breastfeed her child at any time the infant wants, day and night, at least, eight times in 24 hours.
- Empty one breast first before giving the other breast because the baby can get the most nutritious hind or final milk (the final milk has more nutrition than the initial milk, and the initial milk has more water than the final or hind milk). The sign of empty breast looks like; smooth to touch, not hard or not engorged with milk and the breast becomes hanging down.
- During illness and for at least two weeks after the illness increase the frequency of breastfeeding because it helps for the child to recover faster.
- Expose the child to sunshine for 20 to 30 minutes daily and early in the morning, it is essential for better bone growth and development.
- Give exclusive breastfeeding for the child i.e. only breast milk for the first six months, do not give additional food even water except medication (exclusive breastfeeding is recommended and advised to the mother).
Benefits of breastfeeding for children
Breast milk is best for children, and the benefits of breastfeeding extend well beyond basic nutrition. In addition to containing all the necessary vitamins and nutrient to the body, breast milk is packed with disease-fighting substances that protect from illness.
Advantages of breastfeeding for children
- Promote bonding between mother and children.
- Protection against common childhood illnesses and infections.
- It helps for physical and mental development.
- Breast milk makes the children always having a right body temperature.
- It is a nutritionally balanced meal.
- Better survival during the first year of life, including lower risk of sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS).
- Less chance of developing some allergic diseases
- Lower likelihood of being obese as an adult.
- Less chance of developing type 1 diabetes.
- Physical and emotional benefits of breastfeeding directly from the mother's breast due to skin-to-skin contact.
Benefits of breastfeeding for mothers
Like children; mothers also benefited from breastfeeding; as the children benefited from breast milk the mothers also simultaneously benefited when providing breast milk.
Those benefits are the following:
- Facilitates uterine contraction and reducing post-partum bleeding and also help for the expulsion of the placenta.
- Improves postpartum weight loss.
- Emotional benefits from close interaction with the infant.
- Lower likelihood of experiencing postpartum depression, which is seen more often in new mothers who do not breastfeed.
- Less chance of developing certain health conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis, cardiovascular disease, and certain cancers (for example, breast cancer).
- Physical and emotional benefits due to skin-to-skin contact with her infant.
- Breastfeeding helps for child spacing.
Preparation phase, positioning, attachment and sucking techniques of breastfeeding
Preparation
- The mother must be comfortable.
- The babies' abdomen should touch the mother's abdomen.
- The mother should hold her breast with her finger in a C- shape.
- Touch the baby's lower lip by the nipple of her breast to open his mouth.
- The mother should be ready to put the breast quickly into the baby's mouth.
Signs of good positioning during breastfeeding (Figures 1.1. & 1.2)
- The infant's body should be straight.
- The infant's body and head facing the breast.
- The infant's body should be close to her mother's.
- The infant's whole body should be supported.
a) Baby body close and facing

b) Baby whole body supported

Fig. 1.1 Signs of a good positioning.
c) Baby's body away from the mother
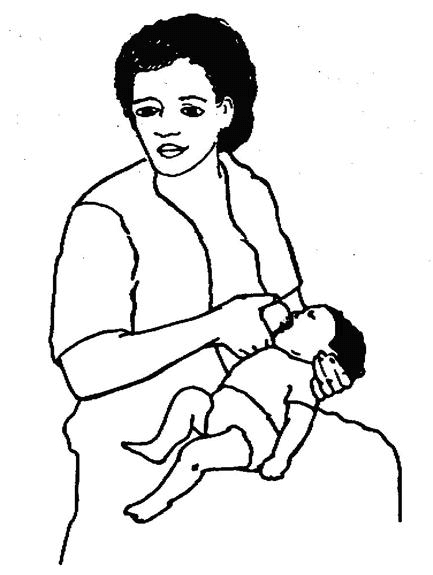
Fig. 1.2. Sign of a poor positioning.
Signs of a good attachment during breastfeeding
- The infant's chin touches the breast.
- The infant's mouth is wide open.
- The infant's lower lip turned outward.
- More areola is seen above the infant's mouth and less areola is seen in the lower part of the infant's mouth.

Fig. 1.3. Signs of good attachment.
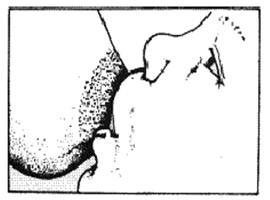
Fig. 1.4. Signs of poor attachment.
Signs of good suckling (Figures 1.3 & 1.4)
- Suckling with slow deep sucks and sometimes pauses.
- See or hear the infant swallowing.
- Infant releases the breast spontaneously.
- Infant appears relaxed, sleepy, and loses interest in the breast.
Infant breastfeeding is affected by the following factors
- When the baby is sick.
- When the mother is sick.
- Both the mother and the baby are sick.
- Malnourished mother.
- An infant who is separated away from her mother.






