Respond means to recognise the child's problem and give an intervention to that problem. First, you should recognise or identify the sign and symptoms of childhood illness and then you provide an appropriate response to that problem. So in this section, you will learn the sign and symptoms and prevention mechanisms of childhood illness, and you will counsel the caregiver and also you will further educate the community to prevent childhood disease.
Chicken Pox (Varicella-Zoster Virus)
Chickenpox (Chicken Pox), also known as Varicella is a very contagious infection caused by the varicella-zoster virus.
Mode of transmission:
- An airborne disease which spreads easily through coughing or sneezing by ill individuals.
- Direct contact with secretions from the rash.
- Contact with articles freshly soiled with the discharges from blisters or vesicles of an infected person.
Signs and Symptoms (Figure 1.7):
- Skin rash often consisting of small blisters all over the body.
- Eruption comes in crops.
- There may be pimples, blisters and scabs all present at the same time.
- Mild fever.
- Sometimes this infection is mild, and only a few blisters are present
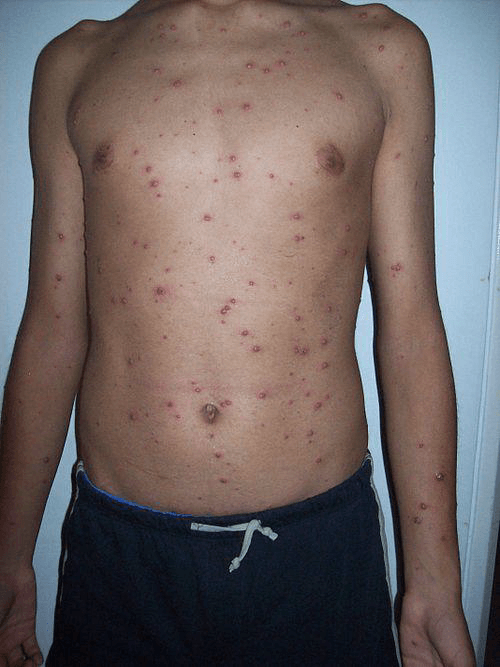
Fig. 1.7. Male with varicella.
Prevention:
- Isolate infected children from school and give child care until all of the blisters are crusted and scabbed.
- Isolate susceptible contacts (i.e. those children who have not had chickenpox disease) from 10 up to 21days following exposure to a case of chickenpox.
- Provide varicella vaccine.
Diarrheal disease
Diarrhoea is defecation of watery stool three or more times per day (or more frequent passage than is normal for the individual).
Mode of transmission:
- Transmission occurs through the fecal-oral route.
- Ingestion of very tiny amounts of faecal material from an infected person through contaminated hands or objects.
- Through contaminated food and water.
- Ingestion of improperly refrigerated, reheated, or contaminated foods.
Signs and symptoms:
- An increased number of stools compared with the child's regular pattern with increased water and/or change in the appearance shape of the stool (form).
- It may be accompanied by nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramping, headache and/or fever.
- Note that breastfed babies may normally have unformed stools.
Prevention:
- Access to safe drinking-water.
- Use of improved sanitation.
- Hand washing with soap.
- Exclusive breastfeeding for the first six months of life.
- Good personal and food hygiene.
- Health education about how infections spread; and rotavirus vaccination.
- Children and family members should thoroughly wash their hands after diaper changes and toilet use.
- Avoid giving to children uncooked food or food which is left for several hours.
- Avoid giving contaminated water from streams or pools, and unboiled water to the children.
Diphtheria
Diphtheria is a bacterial infection caused by Corynebacterium diphtheria, and it can be prevented by immunisation.
Mode of transmission:
Primarily by contact with a person infected with diphtheria. Diphtheria may be transmitted by an asymptomatic person or a carrier. Infectious fluids include discharges from the nose, throat, eye or skin lesions. In rare instances, diphtheria can be transmitted by contact with articles soiled by discharges from the lesions of an infected person.
Signs and symptoms:
- Gradual onset over 1-2 days. Diphtheria usually occurs as a white or grey patch or patches of a membrane surrounding inflammation and soreness in the throat or nose. Glands in the neck are swollen and have Low-grade fevers.
- Diphtheria can occur as skin, vaginal, eye, or ear infection. However, this happens very infrequently and is more common in tropical regions, among homeless persons, and those living in crowded conditions. Diphtheria can be life threatening.

Fig. 1.8. Bull neck: a sign of diphtheria due to enlarged lymph nodes in the neck
Prevention:
- Isolate suspected or exposed patients.
- All unvaccinated children's who are not vaccinated should take diphtheria vaccination.
- Increase community awareness' about vaccination.


