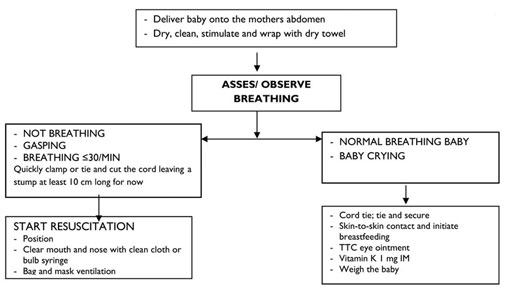
If you are attending a delivery or a baby is brought to you immediately after birth, you should assess for birth asphyxia. Assess the baby after drying and wrapping him or her with a dry cloth. To assess for birth asphyxia, you need to look and listen for breathing patterns.
There are two possible classifications:
It is critical that you treat birth asphyxia quickly; if you don't, the baby may die or may develop complications from which he or she never fully recovers. The table below sets out a summary of the signs of asphyxia and the treatment that should be given.
| SIGNS | CLASSIFY AS | TREATMENT |
|---|---|---|
lf any of the following signs:
30 per minute) | Birth Asphyxia |
gauze or clean cloth or bulb syringe
mask and self-inflating bag
continue giving essential newborn care
has irregular breathing after 20 minutes of resuscitation refer urgently to hospital: continue to resuscitate the baby on the way
if no response (no spontaneous breathing)
|
than 30 per minutes | No Birth Asphyxia |
and 6 weeks |
If there is no birth asphyxia and the baby is crying strongly or breathing more than 30 breaths per minute you should continue with essential newborn care, as summarised in flowchart below.
