What is anesthesia?
Anesthesia is defined as the absence or abolition of sensation, especially that of pain induced by drugs especially as a means of facilitation to surgical procedures.
Anesthesiology is the art and science of rendering a patient insensible to pain by the administration of anesthetic agents and related drugs and procedures. An anesthetist is a qualified health care professional who administers anesthetics to produce total or partial loss of sensation in patients during surgical or diagnostic procedures. Nurse anesthetist is a nurse who specializes in administration of anesthesia and continually monitors patient's reaction to anesthesia, stress of the procedure as well as patient's vital sign in order to maintain the normal physiologic setup throughout the procedures. Anesthetist works in a team contributing her/ his critical role to maximize patient safety, comfort and better procedure out come. Anesthesiologist is a physician specialist and the higher level consultant in anesthesia practice that deals with the most critical patients subjected for surgery and overall management of anesthesia practice in a particular seating.
The three components of anesthesia are analgesia, hypnosis (amnesia) and muscle relaxat;(Fig.1.1). Prevention of undesirable autonomic reflex is also considered as a requirement of anesthesia. Drugs used in anesthesia have varying effect on these three areas; a combination of drugs will have to be used to optimize the whole process of anesthesia.
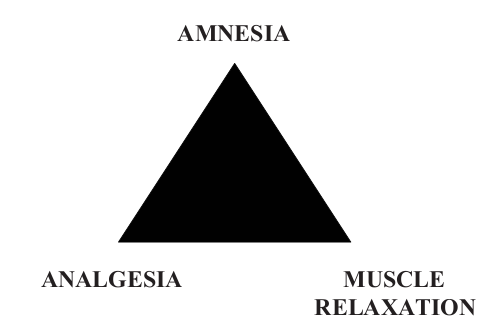
Figure 1.1: Triad of anesthesia.
- Hypnosis: It is a state of sleep or unconsciousness which enable the patient unaware any events during the procedure.
- Analgesia: it is a state of insensitivity to pain with or without loss of consciousness. This component of anesthesia ensures to relieve pain during the procedure.
- Muscle relaxation: Muscle relaxant is drugs which affects skeletal muscle function and decrease the muscle tone by which immobility and relaxation of the skeletal muscle produced and the surgeon will work at ease.
Features of a good anesthetic
- The first objective of anesthesia is the abolition of pain.
- It must be completely reversible.
- It must be as safe as possible. Comfort is important but safety is essential and must come first.
- It should provide good operating conditions. For example, good relaxation for abdominal surgery.
- It should be acceptable to the patient.
Types of anesthesia
- General anesthesia can be defined as a drug-induced reversible depression of the central nervous system resulting in the loss of response to and perception of all external stimuli.
- Regional anesthesia (central regional, peripheral regional) it is the art of rendering a part of the body insensible for surgical operation or manipulation based on the concept that the pain is conveyed by nerve fibers which are amenable to interruption anywhere along their path way.

