As you have learned it in study session 1, you have to assess all the danger signs of the newborn. The table below will help you remind those danger signs.
Remember that the newborn has just come out from the most comfortable uterine environment. It was warm and quiet in the uterus, and the amniotic fluid and walls of the uterus gently touched the baby. You too should be gentle, observant and vigilant with the baby when you handle them and also keep them warm always.
Neonates often present with non-specific symptoms and signs which indicate severe illness. These signs might be present at or after delivery. Initial management of the neonate presenting with these signs is aimed at stabilising the child and preventing deterioration.
The inability of breastfeeding: For a baby who is refusing to breastfeed, you have to identify the underlying causes or other additional symptoms the baby is experiencing. This is because babies will always refuse to breastfeed if there is another associated symptoms (disease conditions) are there, so you have to assess the baby paying deeper attention.
Convulsion: This is an abnormal and purposeless movement of part or the whole body due to an abnormal and untimely impulse from the brain. In neonates and infants, it is characterised by a twitching movement of a single body part, or a jerking movement of all body parts, associated with the synchrony of contraction and relaxation of muscles which causes the body to be hyper-stretched (hyper extended). The condition is more common in babies with high-grade fever, which is greater than 37.5ºC, when the baby gets into a hypoglycemic state, and when dehydrated are the most common causes of this condition. Another undeniable cause is neonatal tetanus.
Lethargy: This is a condition which will occur before drowsiness; on this stage, the baby may not lose consciousness, but he will become sleepy and loses interest for everything. Drowsiness: This is the state which comes after lethargy and before coma; which is characterised by incomplete loss of consciousness, but become sleepy with eyes closed, the eyes will be opened in response to external stimuli and returns again to the sleepy state when the stimuli are removed. Coma: This is the complete state of loss of consciousness, and the baby will not respond to any stimuli. The conditions like hypoglycemia, severe dehydration, and generalised bacterial infections called sepsis are the commonest causes. Sepsis in Neonates is called neonatal sepsis.
Breathing ≤ 30 or ≥ 60 breaths per minute, grunting, severe chest in the drawing, blue tongue & lips, and grunting, or gasping: - These conditions commonly will occur, when the baby had been swallowed amniotic fluid or if there was fetal distress during labour.
The above conditions are the signs and symptoms of neonatal pneumonia. If untreated, the condition can lead to the term apnoea which is a sudden cessation of breathing for about 20 seconds, and neonatal death will be the final result. So, a quick assessment, classifying and referral to the hospital should be a priority. You will learn how you will do this in the last topics of this session.
Hypothermia: This Is a condition when the body temperature of the baby is lower than 35ºC. It can commonly occur in preterm and low birth weight babies. In term babies, if there are conditions related to the non-maturity of the thermoregulatory centre in the brain, they may not adjust themselves with the external temperature, in which case they will feel cold and can also experience shivering. Skin to skin attachment to the mother is the solution.
Hyperthermia: This is a condition in which the baby's body temperature exceeds the normal amount (37.5ºC). It can also be called fever. The main cause of fever is the presence of infectious diseases such as bacterial infection, infection of the umbilicus, neonatal sepsis, pneumonia, malaria and others. If the baby is febrile, you have to assess the baby for the associated signs and symptoms to identify the cause.
Red swollen eyes with pussy discharge: This could be due to the infection of conjunctiva at the time of passage through birth canal especially if the mother were infected by some sexually transmitted infections.
Jaundice: It is the yellowish discoloration of some or all parts of the body. It will occur if there is any condition which can cause destruction of the red blood cells within the baby's body as in ABO incompatibility, which will increase the amount of circulating bilirubin 6mg/100ml of blood, the baby's sclera (white part of the eye), palms, foot creases, as well as general body part (skin) become yellow.
Pallor and bleeding from any site: The baby will become pallor if there is bleeding from any site of the body. The condition may occur due to the immaturity of clotting factors. This is a dangerous condition which will end with the death of the baby due to severe blood loss. So vitamin K administration is a must.
Repeated vomiting, swollen abdomen, no stool after 24 hours: It can occur if there is any obstruction of the alimentary canal at anywhere in the abdomen so assess thoroughly and refer the baby to the hospital.
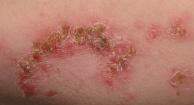
More than 10 skin lesions or rash: The skin lesions on the baby's body which are typically blisters and when ruptured, form a red lesion are mainly caused by bacteria (staphylococcus, and streptococcus pyrogens) and is called Impetigo. Impetigo is commonly seen in the skin fold areas around the diaper areas.

Redness of the umbilicus, or pus discharge from the umbilicus: The umbilicus may get infected with bacteria unless the stump is given proper care. Redness, swelling and sometimes associated with pussy discharge are the commonest signs of infection of the umbilicus.
Neonatal Tetanus: This is another type of infection caused by bacteria called, clostridium tetani. It is a toxin-releasing bacteria which affects the nerves and causes them not to function properly. This malfunction will cause the muscles of the body to stretch and become abnormally rigid.
Because of this, the baby with tetanus experiences rigidity of the extremities and the back, clenching of the gum and abnormal twitching movements on some areas of the body especially the facial muscles. It is one of the causes of neonatal mortality. The mortality rate of tetanus is very high and the survival rate of it is only 1%. This means, that out of 100 babies caught by tetanus, only one baby may get the chance to survive, this is also true under closely monitored and facilitated treatments. The bacteria can get into the body through open wounds, in newborn babies most likely through the umbilical stump. Some cultures in Ethiopia will put cow dung on the newly cut umbilicus. The bacteria lives in the gut of cows as a normal flora and putting the dung on the umbilicus will be a good opportunity for the bacteria to enter into the baby's body and cause tetanus.
